Planning an enterprise migration SEO project makes you worry about losing your hard-earned organic traffic? Your fears make perfect sense. SEO professionals often see their rankings, traffic, and users take a hit during website transitions. A poorly handled migration could slash your traffic by 30-60%.
The good news? Your site migration SEO can maintain stability or boost your traffic if you manage it the right way. Smart enterprise SEO services could help you triple your Google traffic. The SEO market shows promising growth with a projected CAGR of 17% from 2024 to 2030. This makes website migration knowledge crucial for businesses ready to upgrade their digital presence.
A well-laid-out migration keeps your data safe and prevents performance drops when you move to a new domain, hosting platform, or CMS. This site migration checklist guides you through six crucial phases of enterprise SEO optimization services for website migrations. You’ll learn to protect your digital presence during this challenging transition.
Phase 1: Planning Your Website Migration
Website migration SEO success depends on careful planning. Poor preparation can lead to major traffic drops. Research shows that good original planning is the lifeblood of migrations that protect your search rankings.
Define Your Migration Goals And Scope
Good planning starts with clear objectives for your migration project. You need to know why you’re migrating—whether you want better performance, upgraded security, rebranding, or a better user experience. Clear, measurable goals help define what success looks like and guide your decisions throughout the process.
Your migration goals might include:
- Better site speed and performance
- Better user engagement metrics
- Higher search engine rankings
- Better content management
Set realistic project boundaries. Figure out if your migration will change all pages or just certain sections, and set clear metrics to review success. A blog move from a subdomain to a subdirectory might target a 10% increase in organic traffic.
Assign Roles And Responsibilities
The right migration team makes execution smooth. Your project’s size and complexity determine how many people and what roles you need. Enterprise projects with 5,000+ users need more specialized roles than smaller moves.
Your team should have experts in project management, web development, enterprise SEO services, content creation, and IT security. Project managers keep everyone’s efforts coordinated. They make sure the project stays on schedule and within budget.
Each team member needs clear duties and regular meetings to stay organized. Team members must talk often. This helps solve problems that pop up during complex migrations.
Get Departments Working Together
Large organizations face a big challenge when different departments and stakeholders don’t share the same goals. Website migrations can fail when departments pull in different directions.
Get detailed requirements from every department that matters. Send questions early to find out who needs to participate and how their needs shape the project. Create a working group with people from sales, marketing, customer service, IT, and legal.
These people become your champions and keep everyone excited about the project. Talk to executives early about what you need from them. This prevents surprise interventions later. Get active approval from your CEO and other executives instead of just a quiet agreement.
Pick The Right Launch Time
Smart timing reduces problems for users and business operations. Launch during slow traffic periods or seasonal downtimes to limit negative effects. Stop adding new content just before and during migration to avoid complications.
Tuesdays and Wednesdays work best for launches. Monday meetings make launches hard, and mid-week launches give you several workdays to fix issues before the weekend. The 10 AM launch time lets team members settle into work before focusing on migration.
Your site will need some downtime during the switch. Major site changes always cause periods where the site doesn’t work properly. Quick execution becomes vital once you start. Longer migrations risk more damage to your search rankings and traffic.
Phase 2: Pre-Migration SEO Preparation
A solid preparation forms the foundation of any successful enterprise migration SEO project. Your website transition could face major traffic losses without proper pre-migration groundwork. This phase helps you set standards, protect existing assets, and line up technical requirements that safeguard your SEO performance.
Run A Full SEO Audit And Set Performance Standards
Setting performance standards creates the foundation to measure migration success. Start with a complete technical SEO audit that gets into your site’s security, crawlability, internal linking, and speed. This audit helps you establish a baseline to compare post-migration results and reveals issues you should fix before migration instead of moving them to your new site.
Data from multiple sources helps create a complete picture:
- Google Analytics: Export traffic data, conversions, and user engagement metrics from at least the past 12 months
- Google Search Console: Document queries, clicks, impressions, CTR, and average positions
- SEO Tools: Record authority scores, backlinks, ranking keywords, and technical issues
Google Sheets works well to organize your migration standard data. Take screenshots of your organic status to provide visual reference points for later comparison.
Back Up Your Site And Content
Your enterprise migration SEO project needs a complete backup of your existing site. This backup lets you restore your site if problems occur during migration. You should include:
- Complete website files and databases
- Configuration settings and server documentation
- Existing redirect rules from previous migrations
A thorough content inventory comes next. Crawl your site and identify all existing URLs. Multiple methods ensure you don’t miss anything:
- Site crawler tools (like Screaming Frog)
- Analytics platform URL exports
- XML sitemap data
- Backlink analysis tools
Make sure to identify your highest-value pages—pages with substantial traffic, conversions, or quality backlinks need special attention during migration.
Set Up Keyword Tracking And Analytics
Your performance changes need live monitoring systems before migration begins. Create a list of your most important keywords and tag them for migration monitoring. This helps you spot ranking drops right after launch.
These metrics need monitoring:
- Organic traffic and conversions
- Keyword rankings (especially for high-value terms)
- User experience metrics like Core Web Vitals
A dedicated migration dashboard in your analytics platform streamlines post-migration analysis. Your Google Analytics migration plan should document how to maintain consistent tracking through the transition.
Line Up Developers With SEO Requirements
SEO and development teams must communicate effectively for enterprise SEO optimization services. Document all SEO requirements clearly for developers. They need to understand the technical aspects that affect your site’s search performance.
Teams should coordinate these areas:
- URL structure preservation or mapping
- Proper implementation of redirects
- Canonical tags and metadata handling
- Mobile responsiveness requirements
- Page speed optimization
Early access to the staging environment helps you monitor development progress and report issues quickly. The core team meetings and their preferred communication channels, whether ticket management systems or scrum meetings, need your participation.
The staging site needs “noindex” tags and robots.txt blocks to prevent search engines from indexing test pages. SEO audit tools should bypass these directives for thorough testing of the staging environment.
Phase 3: Content and URL Mapping
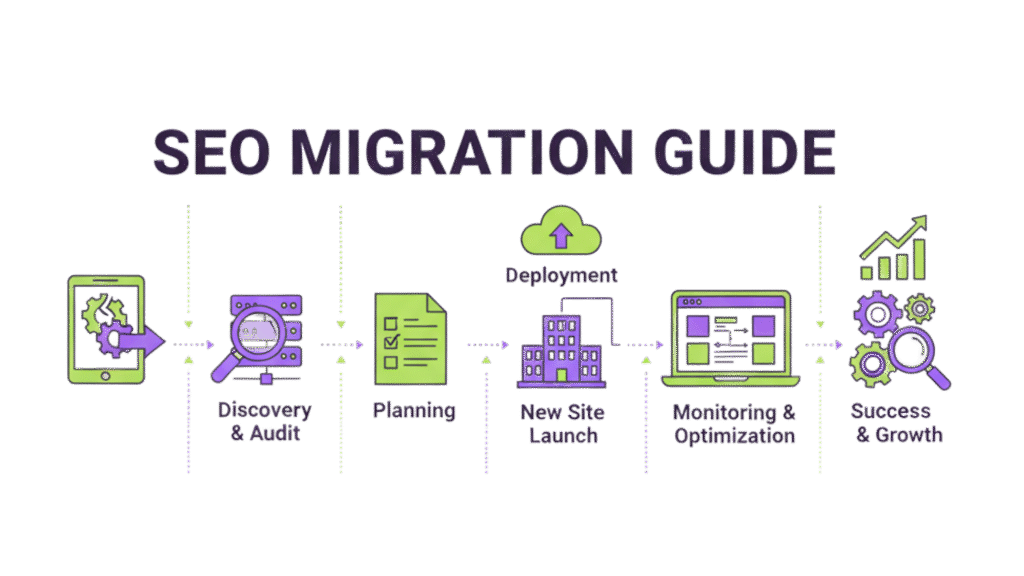
Content and URL mapping are the lifeblood of any enterprise migration SEO project. Your valuable search equity will either transfer to your new site or vanish into the digital world based on this crucial phase. Research shows a strategic redirect plan can prevent the devastating 30-60% traffic drops that often plague website migrations.
Create a Complete Content Inventory
You need complete visibility into what needs migration. Start with a content inventory that catalogs every piece of content on your current website:
- All webpage URLs (from crawling your site with tools like Screaming Frog)
- Blog posts, articles, and press releases
- PDFs and downloadable files
- Images, videos, and other media assets
- Hidden files that may not show up in crawls
The quickest way to generate this inventory is to add ‘/sitemap.xml’ after your domain. This gives you a complete list of your site’s URLs that you can export to a spreadsheet. Document who owns the content, SEO metadata fields, and quality assurance status for each URL.
Identify High-Value Pages And Backlinks
Some pages matter more than others during migration. You need to identify your most valuable content based on:
- Backlink profile strength – Pages with many high-quality inbound links add to your site’s authority. Backlink analysis tools like aHrefs can help you export a list of your “Best by links” pages.
- Organic traffic performance – Look for pages that bring in consistent organic search visitors. Set your Google Analytics date range to the last 12 months, go to Acquisition > Channels > Organic, and set the primary dimension to “Landing Page.”
- Keyword rankings – Pages ranking for important keywords need extra attention to keep those positions.
Add any page with more than one referring domain to your priority redirection list. These high-value pages are the foundations of your migration strategy.
Build Your Enterprise Redirect Mapping Plan
Your enterprise redirect mapping document guides your entire migration. Create a spreadsheet with two key columns: “Redirect From” (old URLs) and “Redirect To” (new URLs).
Enterprise websites with thousands of pages can use these redirection approaches:
- 1:1 redirects – Each old URL points straight to its new URL, keeping maximum SEO value
- Wildcard redirects – Use patterns to redirect groups of similar pages efficiently (e.g., /product/* to /products/)
- Parameter handling – Create specialized redirect rules for URLs with query parameters
Review your mapping document fully once it’s done. Let developers implement wildcard redirects where patterns emerge – it’s more efficient than creating individual redirects for each URL.
Avoid Redirect Chains And Soft 404s
Redirect chains happen when URLs redirect multiple times before reaching their final destination. These chains hurt your site by:
- Slowing down crawling as Google follows only up to five redirect hops before giving up
- Using up valuable crawl budget
- Reducing link equity with each extra hop in the chain
- Making pages load more slowly, which frustrates users
Direct your source URL straight to the final destination URL to prevent redirect chains. Look through server logs for URL redirect histories and use redirect crawler tools to find existing chains.
Soft 404 errors can be just as harmful. These occur when pages look missing to crawlers but don’t send the right signals to search engines. Redirecting old URLs to unrelated pages or your homepage can make Google treat them as soft 404s, which wastes any SEO benefit. Create relevant 1:1 redirects instead of trying to “save” search equity by redirecting to less relevant pages.
Phase 4: Testing in a Staging Environment
A staging environment acts as your migration safety net. You can spot and fix problems before they affect your live site. This testing phase puts your enterprise migration SEO plan through its first ground test and shows problems you might have missed during planning.
Set Up A Secure Staging Site
Think of a staging site as a clone of your website. You can test changes safely without touching your live environment. This duplicate gives you a controlled space to make sure your migration goes smoothly. Here’s what you get with this setup:
- A safe space to test improvements
- Early warning for conflicts between themes, plugins, and other elements
- Protection against downtime on your production site
- A complete testing ground before changes reach users
Make a full backup of your website before you change anything that could affect your site. This backup gives you peace of mind as you step into what might feel like dangerous territory during your first staging experience.
Most hosting providers give enterprise websites staging features you can turn on quickly. Your staging site should look different from your production site. You’ll often see a colored menu bar at the top that helps your team tell the environments apart.
Block Search Engines From Indexing Test Pages
You must stop search engines from finding and indexing your staging site. Without the right protection, search engines might index both staging and production sites. This creates duplicate content problems that hurt your SEO results.
Here’s how to block search engines from your staging site:
- Add a “noindex” meta tag to all staging pages. Your CMS settings make this easy (in WordPress, go to Settings > Reading and check “Discourage search engines from indexing this site”).
- Use an X-Robots-Tag HTTP header with “noindex” for non-HTML content like PDFs and images.
- Use password protection to limit access to authorized team members. This helps prevent unwanted changes and keeps your environment controlled.
Google says you shouldn’t use robots.txt alone to hide staging pages. Robots.txt stops crawling but won’t prevent indexing if pages are found through other means.
Run Technical SEO Audits On The Staging Site
Start your complete technical SEO testing once your staging site is secure. Your staging setup should match your production environment’s server specs, memory, and processing power. This creates the right conditions for accurate testing.
Server settings might block standard crawling tools from accessing your staging site. You can fix this by setting your crawling tools (like Screaming Frog) to ignore robots.txt files in their settings. Most professional crawling tools let you add login details if your staging site needs them.
Focus on these areas during your audit:
- Site structure and navigation
- Page load speeds and Core Web Vitals metrics
- Mobile responsiveness
- URL structure implementation
- Redirect functionality
Development websites usually run slower than production sites. Lower your crawl speeds in testing tools to avoid overloading the server.
Fix Broken Links, Metadata, And Internal Links
Broken links make users unhappy and damage your SEO rankings. They hurt user experience and site credibility. Tools like Broken Link Checker plugins or services like Semrush and Ahrefs help find these problems in your staging environment.
Check that all pages have the right titles, descriptions, and canonical tags in their metadata. Look at header tags to ensure proper hierarchy and implementation.
Your site’s crawl depth depends heavily on internal linking. Pages with high crawl depths (5+) might never show up in Google searches or could get less authority because they’re too far from important pages. Review your internal linking structure to:
- Create logical content clusters around key topics
- Make high-value pages easy to find
- Keep crawl depths reasonable across the site
- Ensure breadcrumb navigation works right
Finding and fixing these issues in your staging environment reduces the risk of SEO performance drops after migration.
Phase 5: Launch and Go-Live Checklist
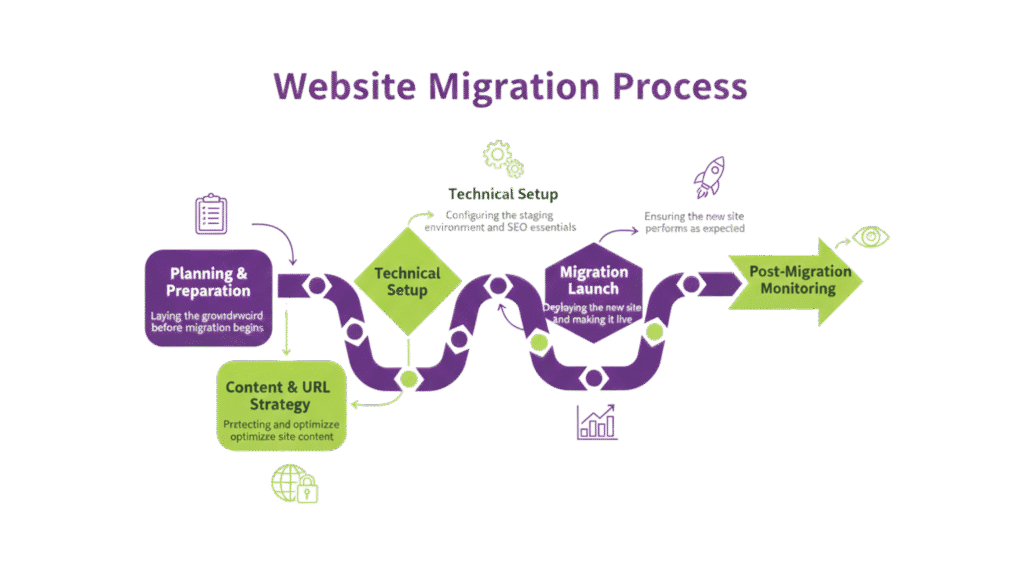
The launch phase marks the peak of your enterprise migration SEO preparation. Your planning now turns into action. The time has come to execute your go-live strategy with precision after completing tests in the staging environment. This approach helps minimize potential traffic drops.
Remove Noindex Tags And Robots.Txt Blocks
Removing all temporary website blocks is vital when you’re ready to launch. Look for any remaining noindex tags used during development that prevented search engines from indexing your staging site. Many websites make the common mistake of launching with noindex tags still active, which makes them invisible to search engines.
Your site readiness checklist should include:
- CMS settings check (WordPress users should go to Settings > Reading)
- HTML inspection for meta robots tags
- X-Robots-Tag directives review in HTTP headers
Search engines won’t index your new pages if these blocks remain active, which nullifies all your migration work.
Submit Updated XML Sitemap
Your new XML sitemap needs immediate submission to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools after launch. This helps search engines understand your site structure and speeds up new URL discovery. Your sitemap should only include URLs with 200 status codes and contain all available site URLs.
The robots.txt file needs updating to point to your new sitemap location. While a sitemap submission doesn’t guarantee complete indexing, it speeds up the process significantly.
Monitor Crawl Errors And Indexing In Real-Time
Careful monitoring becomes key after implementation. Google Analytics and Search Console should send automated alerts about traffic changes. Search Console’s Coverage report reveals crawl errors like 404s, parsing issues, or URL structure problems that need quick fixes.
The URL Inspection Tool helps verify individual page indexation status and fix any fetch errors.
Promote Your New Site With PPC Or Email Campaigns
Your launch needs strategic promotion to boost visibility. PPC campaigns can target specific demographics and bring quality traffic to your newly migrated site. Email newsletters work well to tell your audience about the changes and get them to visit.
Users feel more motivated to explore your new site when you highlight better functionality and faster loading times. This approach helps balance any temporary organic traffic changes during the transition.
Phase 6: Post-Migration Monitoring and Optimization
Your site needs vigilant monitoring after going live – this represents the final crucial phase of enterprise migration SEO. Search visibility preservation demands careful performance tracking, even with the most detailed migration execution.
Compare Pre- And Post-Migration Performance
Your performance metrics need close tracking against pre-migration standards after migration. The first 2-4 weeks require weekly KPI reports, and monthly reports should follow for 1-3 months. These critical metrics deserve comparison:
- Pre- and post-migration rankings for priority keywords
- Site speed measurements on key templates
- User experience metrics (bounce rate, time on site)
- Traffic week-over-week and month-over-month
- Number of indexed URLs over time
Google needs time to relearn your website structure, which might cause a slight traffic decrease. Despite that, any substantial drops without recovery call for immediate deeper analysis.
Fix Any Broken Redirects Or Missing Pages
The first couple of weeks post-migration demand regular re-crawling of your priority URL list. This verification ensures HTTP response codes and redirect destinations work as intended. Redirect rules can unexpectedly stop working, even when they performed perfectly on launch day.
Search Console helps identify crawl errors that need quick fixes for broken redirects or missing pages. Note that 404 errors can substantially affect your site’s SEO by lowering search rankings.
Update Technical Documentation
Technical documentation needs revision after migration completion to maintain accuracy. Future optimization efforts and troubleshooting rely on this documentation. Your updated documentation should include:
- Spreadsheet of 301 redirects (old and new URLs)
- Updated XML sitemap
- Title tags and meta descriptions
- Performance metrics comparison report
- Current robots.txt status
Implement Ongoing SEO Maintenance Practices
Scheduled website crawls help spot new technical issues early. Quarterly redirect audits catch broken redirects or redirect chains. On top of that, keeping dated records of all redirect decisions and performance notes helps future reference.
Tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, and Ahrefs serve as monitoring systems to track metrics and spot performance-affecting anomalies. Your enterprise migration SEO project’s long-term success depends on consistent monitoring and maintenance.
Conclusion
Website migration marks a turning point for your online presence. A well-executed migration protects your SEO investments and can boost your search visibility. The six-phase approach gives you a complete roadmap to protect your hard-earned rankings.
Good planning is your best defense against traffic drops. Your site needs proper pre-migration preparation, detailed URL mapping, and full testing in a staging environment. Strategic launch execution and close post-migration monitoring will help you succeed.
Don’t see migration as a threat – it’s a chance to make things better. This process lets you fix technical issues, build better site architecture, and boost user experience. These changes lead to stronger SEO performance.
Want to migrate your website without losing traffic? RankFast’s SEO content optimization services can guide your site’s transition. Our website traffic analytics tools track performance throughout the process. We also offer PPC strategies to maintain traffic during changes. Pick a partner with expertise to protect your digital investment.
FAQs
What are the most critical elements to focus on during a website migration to prevent traffic loss?
The most critical elements are proper 301 redirect mapping, preserving site structure and internal linking, maintaining page speed and mobile responsiveness, and ensuring all high-value pages are properly redirected and indexed.
How can I track the success of my website migration?
Track key metrics like organic traffic, keyword rankings, indexation status, and user engagement before and after migration. Set up weekly reports for the first month, then monthly reports for 1-3 months to compare performance against pre-migration benchmarks.
What should I do if I notice a significant traffic drop after migration?
If you notice a significant traffic drop, immediately check for technical issues like broken redirects, improper indexing, or crawl errors. Review your redirect mapping, ensure your sitemap is up-to-date, and use Google Search Console to identify and fix any problems quickly.
Is it necessary to inform Google about my website migration?
Yes, it's important to inform Google about your website migration. Use Google Search Console to register the domain change and submit your updated XML sitemap. This helps Google understand the changes and can speed up the re-indexing process.