AI has changed how you rank in search results by connecting related concepts through patterns instead of keywords. The numbers tell an interesting story – AI Overviews now show up in 11-13% of U.S. Google queries, compared to 6.5% in early 2025. Pages that appear below these AI-generated summaries see their clicks drop by 34.5%. The old keyword-focused strategies don’t work anymore. Entity SEO now care more about understanding context than counting keywords. Google wants to give answers based on context, not just words. Modern algorithms do more than match search terms – they understand meaning and find connections between entities in your content.
The Knowledge Graph creates the foundations for this semantic understanding. It turns concepts into distinct, connected entities that search engines can spot in different situations. Your business needs to build authority through detailed, context-rich content to succeed in this new search environment.
What Is An Entity In SEO?
Search engines recognize and understand an entity as a distinct, singular, unique, and well-defined thing or concept. These entities are the building blocks that search engines use to categorize and make sense of online information.
Entities represent actual concepts with contextual meaning, unlike traditional keywords. Search engines can connect different pieces of information when you optimize for entities. This creates a web of understanding that goes beyond simple word matching.
What Makes Something an Entity?
An entity in SEO must meet these criteria:
- Uniquely identifiable with a specific ID in a database
- Distinguishable from other entities
- Well-defined and recognizable
- Able to exist in relation to other entities
Search engines use unique identifiers like “MREID=/m/23456” or “KGMID=/g/121y50m4” in Google’s system. These IDs help organize and retrieve information about specific topics.
Types of Entities You Should Know
Entities cover a wide range of concepts, including:
- People (Patrick Swayze, Warren Buffett)
- Places (New York, Brown University)
- Organizations (Google, Berkshire Hathaway)
- Events (Brighton SEO)
- Products (MacBook)
- Abstract concepts (Quantum Physics)
Google identifies approximately 8 billion different entities, and this number keeps growing. This massive database powers the semantic understanding that drives modern search.
Beyond Keywords: Why Entities Matter
Your SEO strategy remains limited to matching specific words or phrases when you focus only on keywords. Entity SEO lets you build context and meaning around these keywords.
The keyword “Apple” could mean the fruit, the technology company, or something else entirely. Search engines determine the intended meaning based on surrounding context. Users receive more relevant search results thanks to this disambiguation process.
On top of that, it helps search engines understand relationships between concepts. Entity SEO would recognize connections between your managed security service and related entities like “cyber security,” “threat detection,” and “incident response”.
Entities and Google’s Knowledge Graph
Google’s Knowledge Graph serves as a database of entities and their relationships. Google can confidently display information about your brand or topics in Knowledge Panels when your content signals strong entity connections. These prominent search features appear for entities that Google recognizes well.
Your content’s meaning becomes clearer to search engines with entity optimization. This approach lines up with search’s fundamental change and improves your chances to appear in high-value SERP features.
Search engines evolve to understand user intent better each day. You should focus on establishing clear entity relationships in your content rather than just targeting keywords. This entity-based approach becomes valuable especially when you have AI-powered search features becoming more prominent.
What Makes Entity SEO Different from Traditional SEO
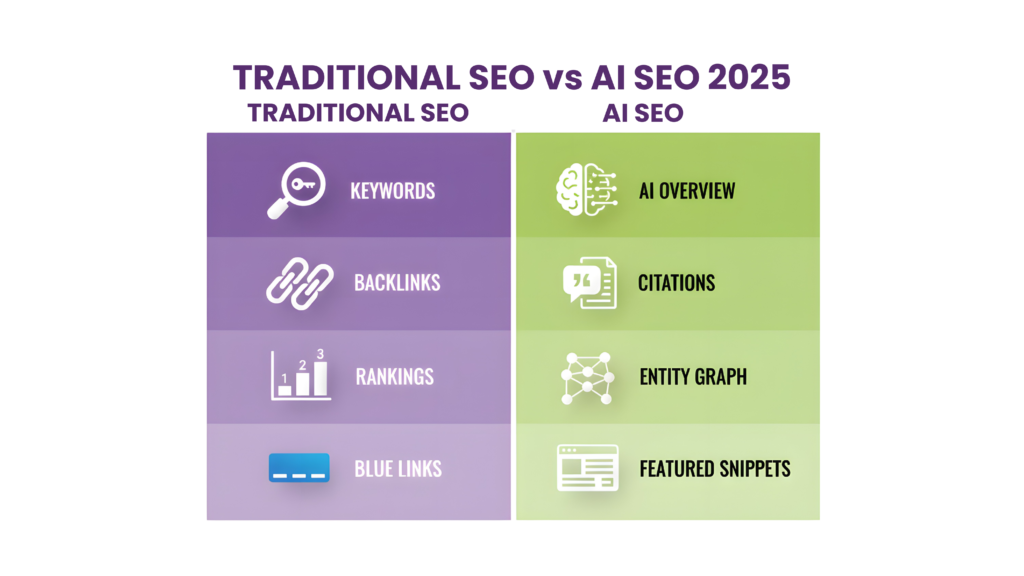
The main difference between traditional and entity SEO shows up in how search engines handle information. Traditional methods see content as keyword collections, while entity SEO looks at how concepts connect to each other. This gives search engines a better way to understand context.
Keywords vs Entities: Understanding The Change
Traditional SEO revolves around optimizing keywords. We placed specific words throughout content based on search volume and keyword difficulty. This method, which ruled search practices before 2010, focused on:
- Exact keyword matching
- Keyword density and placement
- Simple on-page optimization tactics
- Backlinks and authority signals
This keyword-focused approach worked well before but creates disconnected topics across websites. It makes it harder to build real topical authority. Traditional SEO doesn’t deal very well with unclear language. It can’t tell if “Apple” means the fruit or the tech company without more context.
Entity SEO takes a different path by building meaning between concepts. Keywords are just character strings, but entities are actual “things” with real meaning. This change brings new ways to optimize your content:
Search results used to show pages that mentioned target keywords. Now, Google uses entity understanding to pull from more sources. Pages that cover related topics can rank even without exact keyword matches. Your content can rank for searches that don’t appear word-for-word in your text.
This rise lets search engines look beyond simple keyword matching. Users now get better results based on what they want rather than just what they type.
How Google’s Knowledge Graph Changed Search
Google’s Knowledge Graph, introduced in 2012, revolutionized search by replacing many ranking algorithms. This smart database holds billions of entities and their connections. Google now knows what people, places, and things are – not just their descriptions.
The Knowledge Graph has grown fast. It jumped from 570 million entities and 18 billion facts in 2012 to about 8 billion entities and 800 billion facts in less than ten years. This rapid growth shows why entity-based optimization matters more in your SEO strategy.
The Knowledge Graph works through a structure called ontology, with three main levels:
- Entity catalog – Storage for all identified entities
- Knowledge repository – Where entity attributes combine from different sources
- Knowledge Graph – Where entities connect through defined relationships
This setup helps Google understand that a search for “Eiffel Tower” means the famous Paris landmark – not just web pages with those words. Google says the Knowledge Graph helps people find “things, not strings”.
These changes brought new features to search results like knowledge panels that show quick facts about entities right on the results page. The “People also search for” feature shows related entities and creates new ways for users to find your content.
Your SEO strategy needs to go beyond keywords. You must establish your brand or topic as a known entity that connects to other relevant entities. Building complete context around your subject helps search engines grasp not just your target keywords but what your content really means.
How AI and NLP Power Entity Recognition In Search
AI models are the foundation of modern search systems. They have changed how search engines identify and process entities in your content. NLP technologies have improved by a lot. Search engines now understand meaning instead of just matching text patterns.
Role of BERT and MUM in Semantic Understanding
Google’s launch of BERT in 2019 changed entity SEO forever. Earlier algorithms looked at text in order. BERT looks at words from both directions. It sees what comes before and after at the same time. This breakthrough helped search engines learn language nuances with amazing accuracy.
BERT’s biggest gift to entity SEO is how it understands context. When it processes a query, BERT studies how words relate to each other. This helps it figure out their meaning in specific situations. To cite an instance, in phrases like “Apple founder” or “New York Giants,” BERT helps Google spot the right entities without needing exact matches.
Google then launched MUM in 2021. It’s an even smarter way to spot entities. MUM is 1,000 times more powerful than BERT and works with 75 languages at once. This multi-language base helps MUM understand and create language with incredible skill.
MUM stands out for your semantic optimization because:
- Multimodal processing – MUM can study text, images, and soon video and audio together. This creates a complete picture of content
- Cross-language capabilities – MUM shares knowledge across languages, removing language barriers in search
- Complex query handling – MUM gets complicated questions that need information combined from many sources
Google keeps growing its knowledge graph through these advanced models. It combines information from different media types and languages. Your content strategy needs to grow beyond text. You must think about how entities show up in all types of content.
Entity Disambiguation in Conversational Queries
Entity recognition faces a tough challenge. It must figure out if “Paris” means the French capital or someone’s name based on context. Modern AI systems are great at this task. They use context clues to get it right.
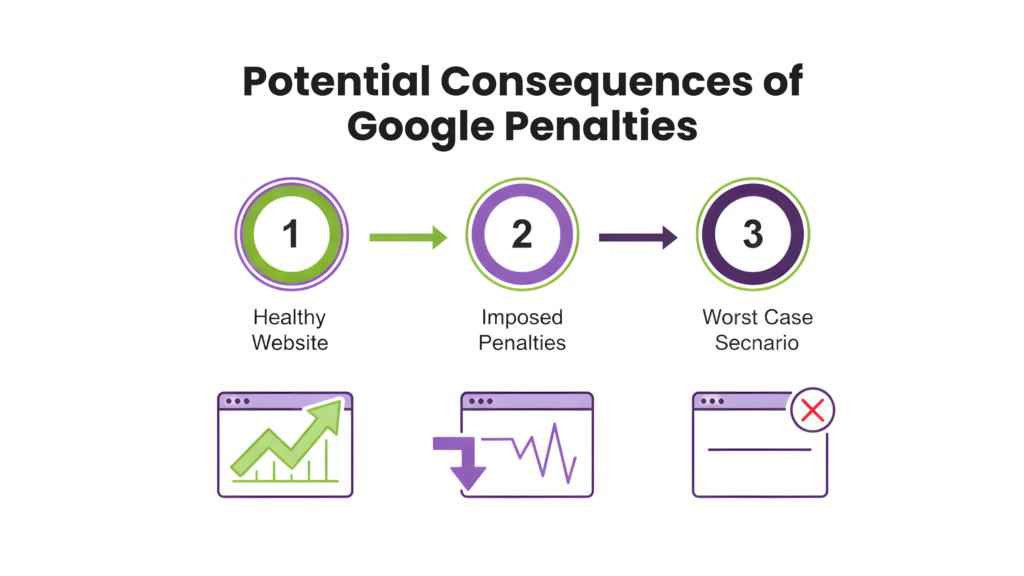
Entity disambiguation happens through these connected steps:
- Context analysis – The system looks at nearby words to understand context
- Candidate generation – The system finds possible entity matches from what it knows
- Probabilistic ranking – AI models rate how well each candidate fits based on context clues
Let’s say someone mentions “Giants” while talking about the NFL season. Entity disambiguation helps the system know they mean the New York Giants football team, not the San Francisco Giants baseball team.
Virtual assistants and voice search need entity disambiguation. This is crucial for on-device processing with limited resources. Studies show using deterministic approximations to probabilistic grammars in finite-state transducers can reduce word error rates by 10% for complex entity queries.
Search engines now understand entity relationships even when users ask questions in casual ways. This matters for your website’s topical authority. Your content should build clear entity connections through complete topic coverage instead of just matching exact keywords.
Deep learning models like transformers keep making entity recognition better. These systems learn features from huge datasets on their own. They’re getting closer to understanding things the way humans do.
Search interfaces are becoming more conversational and context-aware. Your entity SEO strategy must change too. Focus on how concepts connect instead of isolated keywords. This matches how modern AI-powered search systems actually work with information.
Building Topical Authority Through Entity Clusters
Your digital presence in Google’s Knowledge Graph needs strategic topic clusters. This approach surpasses simple keyword optimization and creates semantically connected content networks that signal topical authority to search engines.
Creating Content Hubs Around Core Entities
Content hubs are carefully curated collections of content centered around specific entities or topics. They unite related materials into well-laid-out structures that help users and search algorithms find information. This unity makes your content more searchable, which increases website traffic and deepens brand awareness.

The hub-and-spoke model works best for entity SEO:
- Core pillar page: A detailed guide covering your primary entity or theme broadly
- Supporting cluster pages: More specialized content addressing related subtopics
- Semantic connections: Clear relationships between all content pieces
Search engines reward higher rankings to sites that showcase expertise through content housed under one topical umbrella. This structured approach matches search intent and establishes topical relevance better than disconnected content.
Using Internal Linking To Reinforce Context
Internal linking strengthens your entity clusters by defining semantic relationships between content pieces. Contextual links connect ideas and guide readers to related content that reinforces your site’s expertise on specific topics.
Your semantic optimization needs these principles:
- Link from pillar pages to all supporting cluster pages
- Every cluster page must link back to its pillar
- Create cross-links between related cluster pages where logical connections exist
- Use descriptive anchor text that communicates entity relationships
This interconnectivity establishes a logical hierarchy, clarifies topical depth, and helps crawlers interpret relationships between pages. Combined with structured data, this approach creates a strong semantic data layer (Content Knowledge Graph) that supports both traditional and AI search.
Avoiding Content Cannibalization With Clear Entity Focus
Search engines don’t deal very well with multiple pages competing for the same keywords or entities. This internal competition weakens your search rankings and confuses users and search algorithms.
Your entity SEO strategy should:
- Create a proper content strategy with distinct entity focus for each page
- Develop a keyword tracking system to avoid targeting similar terms across multiple pages
- Conduct regular content audits to identify and resolve competing pages
You should choose a preferred page for each entity when cannibalization issues appear. Then unite competing content or implement 301 redirects where appropriate. Clear entity boundaries between content pieces prevent overlap while establishing semantic connections.
Strategic internal linking and well-laid-out entity clusters help search engines understand your topical authority. Users benefit from detailed, easily navigable information resources.
Using Structured Data To Strengthen Entity Signals
Structured data works as your secret weapon to tell search engines exactly how different parts of your website connect. Schema markup creates a layer that machines can read. This helps search algorithms identify and group your content’s topics accurately.
Schema Types: Organization, LocalBusiness, Product
The right schema type helps search engines better understand your content. Organization schema builds your business identity through properties like name, logo, contact details, and social profiles. This basic markup makes knowledge panels possible and builds your brand’s recognition.
Local businesses can add location details to their organization markup with LocalBusiness schema:
- Physical address and geo-coordinates
- Operating hours and accepted payment methods
- Service areas and specific departments
Product schema signals key details about items you sell through attributes like name, description, brand, price, and availability. Your chances of showing up in rich results go up with product schema. Companies like Rotten Tomatoes saw their click-through rates jump 25% on pages using structured data.
How Structured Data Connects To The Knowledge Graph
Structured data links your content directly to Google’s Knowledge Graph—a massive database with over 500 billion facts about 5 billion entities. Schema markup turns your content into a format that search engines process and add to this knowledge network easily.
Structured data builds entity relationships by:
- Giving unique identifiers (@id) to entities on your website
- Setting clear relationships between entities through schema properties
- Connecting to external knowledge bases with the sameAs property
This method creates what experts call a “Content Knowledge Graph”—a network of connected entities that AI systems use to grasp your content’s meaning and context.
Tools to Validate and Test Schema Markup
Testing tools help you check your structured data before going live. Google’s Rich Results Test shows if your schema can create Google rich results. You can preview these enhanced results right in the tool.
The Schema Markup Validator checks if you follow Schema.org standards without focusing on specific features. This gives you a full picture of whether your structured data follows proper syntax and guidelines.
Schema standards change often, so regular checks matter. Google lists all structured data updates on their “What’s new” page and Webmasters Blog. Keeping track of these changes helps your entity signals stay strong as search technology grows.
Off-Site Signals That Boost Entity Recognition
Your brand’s authority gets a boost from signals beyond your website. Search engines use these off-site factors to identify and classify your brand within the knowledge graph.
Unlinked Brand Mentions In Authoritative Sources
Unlinked mentions – brand references without hyperlinks – play a vital role in entity SEO. Google’s patent recognizes “implied links” (unlinked mentions) just like traditional hyperlinks. Your brand’s mentions in reputable publications signal authority even without direct links.
The words around your brand mentions create semantic signals that help Google understand your topic relevance. These references build your E-E-A-T profile, especially on high-authority sites.
Social Media Consistency And Co-Citations
Brands with consistent social media presence see remarkable results. They get 5x more engagement per post than inconsistent publishers. Regular social posting creates a snowball effect for your brand recognition.
Co-citation happens when others mention your brand next to competitors or related entities. These mentions create valuable semantic connections that place you within your industry’s entity cluster.
Claiming And Optimizing Google Business Profile
Google Business Profile stands out as a crucial entity signal. Industry experts say an optimized GBP affects about 33% of Local Pack rankings and 15% of local organic results.
To boost this entity signal:
- Fill out your profile completely
- Pick accurate primary and secondary categories
- Keep NAP (name, address, phone) details consistent across all citations
Future-Proofing Your SEO Strategy with Entity Optimization
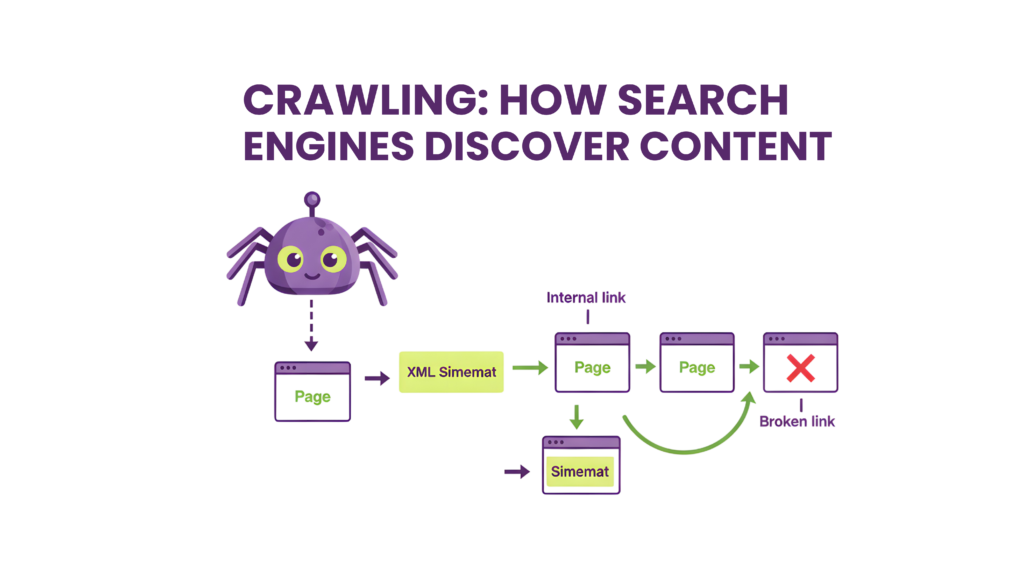
Your entity SEO strategy needs to adapt as search evolves. Changes that favor semantic understanding over traditional ranking signals are coming. You need to prepare now to stay visible through algorithm updates.
Why Backlinks Are Losing Importance
Google’s Gary Illyes made it clear that backlinks “haven’t been in the top three [ranking factors] for some time”. This marks a transformation from 2016 when backlinks ranked among the top three factors with content and RankBrain. Google can now find and rank sites that have exceptional content with no backlinks.
Duy Nguyen confirmed this trend during a Google SEO Office Hours session. He stated that “backlinks as a signal has a lot less significant impact compared to when Google Search started many years ago”. Link building still matters, but its importance keeps dropping as entity signals become more vital.
Preparing for AI Overviews and Answer Engines
AI Overviews reach more than 2 billion monthly users in over 200 countries. This has changed how people search completely. Google shows AI-generated overviews in 18% of searches, and 58% of U.S. adults say they’ve seen these results.
The digital world demands new strategies to stay visible:
- Build topic clusters instead of isolated keyword posts
- Use internal linking to connect related subjects
- Highlight credentials through author bios and transparent sourcing
Entity SEO for Voice Search and AI Assistants
Voice search keeps growing fast. Experts predict more than 8 billion voice assistants will be used worldwide by 2025. Entity optimization helps voice search performance because AI assistants prefer clear, contextual answers.
Users phrase voice searches like natural conversations rather than keyword strings. Entity optimization helps voice assistants understand these conversational queries and pick your content as the answer.
Want to make your SEO strategy future-proof with entity optimization? Visit RankFast to learn about building semantic search visibility that lasts through algorithm changes.
Conclusion
The radical alteration to entity SEO has reshaped how search engines understand and rank your content. Your SEO strategy needs to go beyond basic keyword optimization and welcome semantic relationships between concepts. Search engines now see your content as a network of connected entities instead of isolated keywords. You need complete topic coverage to establish authority.
Entity optimization works better than old approaches. Modern AI-powered search systems process information this way naturally. Your content can rank for related queries without exact keyword matches. This matters even more now that AI Overviews and voice search reshape the digital world.
You’ll win in this new era by building clear entity relationships through strategic content clusters, resilient internal linking, and complete schema markup. Your brand signals must stay consistent across all digital touchpoints to strengthen your position in Google’s Knowledge Graph.
Search engines now value context more than traditional ranking signals like backlinks. Companies like higher education SEO agency that adjust their SEO approach to focus on entity relationships will stay visible whatever the algorithm updates bring.
Want to reshape your digital presence through entity-focused SEO? RankFast’s SEO services help you build the semantic framework spatially as SEO agency for education. Search now focuses on understanding rather than matching, and knowing how to build strong entity connections will determine your future visibility and success.
FAQs
Q1. What is entity SEO and how does it differ from traditional SEO?
Entity SEO focuses on optimizing for concepts and relationships rather than just keywords. It helps search engines understand the context and meaning of your content, allowing you to rank for related queries even without exact keyword matches.
Q2. How has AI impacted search engine optimization?
AI has transformed SEO from simple keyword matching to understanding user intent and context. Search engines now use advanced algorithms to analyze content semantically, prioritizing comprehensive topic coverage and entity relationships over keyword density.
Q3. What are some key strategies for implementing entity SEO?
Key strategies include creating content hubs around core topics, using internal linking to reinforce context, implementing structured data markup, and maintaining consistent brand signals across digital platforms. Building clear entity relationships is crucial for establishing topical authority.
Q4. How can businesses prepare for AI-generated search results?
To prepare for AI overviews and answer engines, focus on building comprehensive topic clusters, use internal linking effectively, and highlight your expertise through author bios and transparent sourcing. Optimize for conversational queries to improve performance in voice search and AI assistants.
Q5. Are backlinks still important for SEO?
While backlinks are still a factor, their importance has diminished compared to earlier years. Search engines now place greater emphasis on content quality, user experience, and entity signals. Focus on creating valuable, entity-rich content that naturally attracts mentions and links from authoritative sources.